Autonomous robotic synthesis of powders and thin films
Description
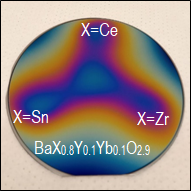
The ExploraMat autonomous research platform allows the synthesis of materials in the form of powders or thin films, their structural and chemical characterization, as well as the measurement of their electrical properties. The strength of the platform is to be able to produce several dozen samples from solutions containing up to 8 different cations and to be able to optimize a given property using all the characterizations carried out. It is an autonomous platform in that the synthesis, characterization and analysis of data as well as optimization are carried out without human intervention. The platform is currently focused on dielectric measurements on oxide materials, but its modularity makes it possible to consider other applications such as photocatalysis, ionic conduction properties, etc.
Location
SPMS Laboratory – CentraleSupelec / CNRS / Université Paris-Saclay/
Contacts
Platform manager / Coordinator of the associated targeted project : Guilhem DEZANNEAU
Technical characteristics
The ExploraMat autonomous research platform enables the production of materials in the form of powders or thin films. The range of compositions is extremely vast since more than 8 stock solutions can be dosed together as well as several powders, resulting in very complex formulations. The materials produced will then be characterized automatically using:
- Optical imaging to be able to determine the quality of the deposit in terms of homogeneity,
- X-ray diffraction makes it possible to trace structural properties,
- Ellipsometry, to go back to the optical properties and thickness of materials,
- Raman spectrometry to determine residual species or surface reactivity,
- Electrical measurements, after the deposition of contacts by inkjet.
All of the characterizations carried out in automatic mode will be subject to subsequent processing to extract relevant information on the materials produced in terms of composition, phase, microstructure and properties.
After the completion of a certain number of syntheses intended to feed a database, the syntheses will be reprogrammed automatically in order to optimize the initial target properties.
Associated targeted project